 You most definitely know what Lyme disease is if you live in Central Massachusetts. Transmitted by deer ticks, you may not have experienced Lyme directly, but the epidemic proportion to which this disease exists within our area has created broad public awareness.
You most definitely know what Lyme disease is if you live in Central Massachusetts. Transmitted by deer ticks, you may not have experienced Lyme directly, but the epidemic proportion to which this disease exists within our area has created broad public awareness.
What you may not be aware of are the other tick-borne diseases that are transmitted in Middlesex County and Worcester County. Anaplasmosis, Babesiosis, Powassan Virus and Rocky Mountain spotted fever to name a few.
Babesiosis in Middlesex County Mass
Among the plethora of tick-borne diseases spread by deer ticks is Babesiosis. While relatively rare, this disease is mostly found in the Northeastern and the Midwestern United States. So much so, that the CDC reports 95% of Babesiosis cases in the US in 2013 occurred in only seven states; including Massachusetts. While Massachusetts reached an all-time high with 520 confirmed and probable cases of Babesiosis in 2014, we still have had a large number of cases of Babesiosis in 2015 with 445 confirmed and probable. Middlesex County was among the top 5 counties in the state with 65 cases of Babesiosis in 2015.
While there is some growth in awareness of Babesiosis in our area, there is a great deal of important data the public needs to be reminded of to help prevent Babesiosis and recognize it. Disclaimer before reading further: anyone can become sick from Babesiosis during any month of the year.
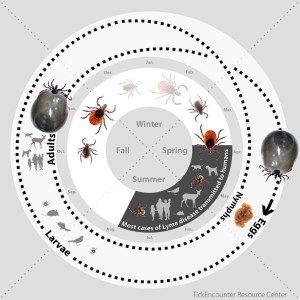
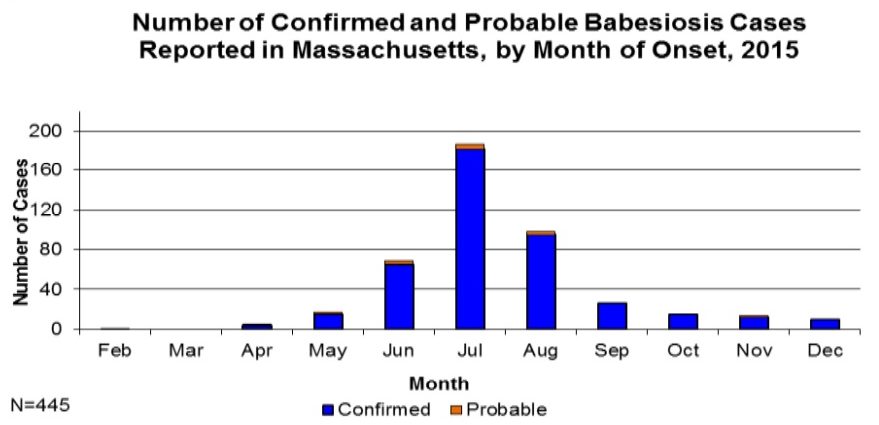
Seasonality of Babesiosis in Central Massachusetts
Tick-borne diseases have a predictable peak season due to the tick life cycle. For most tick-borne diseases, larval and nymph ticks have to have their first blood meal to become infected. The known exception is Borrelia Miyamotoi which can be passed from a tick mother to her offspring. For Babesiosis, this first blood meal is essential to becoming infected, making June, July, and August more common for the spread of the disease than other months of the year.
Health Dangers of Babesiosis
Babesiosis is a parasite transmitted to humans by the bite of an infected deer tick. Many people who have Babesiosis feel fine and have no symptoms. Others experience flu-like illness or severe, life-threatening illness if Babesiosis infects the red blood cells. The variety of symptoms felt can also be tricky, Massachusetts Department of Public Health reported the symptoms of 2015 Massachusetts’ cases as:
- 72% fatigue
- 68% fever
- 58% depression
- 50% muscle aches
- 49% chills
Babesiosis is Discriminatory
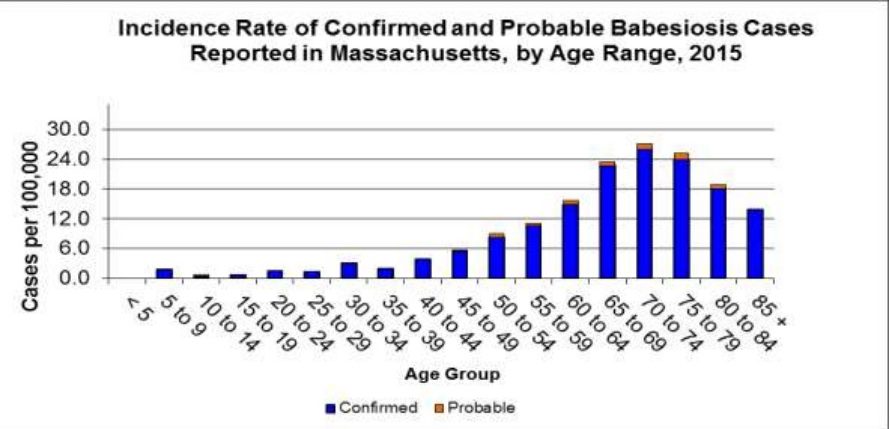
While anyone can become ill from Babesiosis, clinical illness from Babesiosis is more common among a certain portion of the population. Those age 60 or older are at the greatest risk for clinical disease. Also, those without a spleen, weakened immune system, or those with other serious health issues such as liver or kidney disease. Note the chart below; there is a clear age discrimination for the onset of clinical illness from Babesiosis in Massachusetts 2015 cases. If you are within this high-risk category, you should be taking extra precautions to avoid deer ticks, especially during the peak seasons as shown above.
I am committed to providing you the best most up-to-date information on the threat of tick-borne diseases in Central Mass. Stay tuned for the latest on ticks in the area. Be sure to follow the 6 C’s tick control to make certain your yard is not inadvertently attracting ticks.
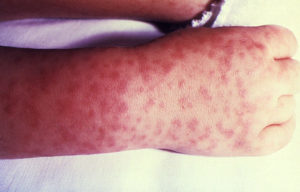
 Rocky Mountain Spotted fever (RMSF) is so far not as common in Massachusetts as Lyme disease. This can make it extra dangerous as physicians and patients do not readily know the risks, signs, and symptoms.
Rocky Mountain Spotted fever (RMSF) is so far not as common in Massachusetts as Lyme disease. This can make it extra dangerous as physicians and patients do not readily know the risks, signs, and symptoms.